Mechanism of a Chemical Reaction
Mechanism of a Chemical Reaction: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Mechanism of a Reaction, Elementary Reactions, Complex Reactions, Rate Determining Step & Formation of Intermediate during a Chemical Reaction etc.
Important Questions on Mechanism of a Chemical Reaction
For next two question please follow the same
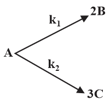
If in a unimolecular reaction, products takes place according to the mechanism
I.
II.
where are the rate constants and P, and stand for product molecule, normal molecules of reactants and activated molecules of reactants respectively.
Which of the following expressions are correct?
The reaction between and occurs in the following steps:
The reaction intermediate in the reaction is
Identify the correct potential energy vs reaction co-ordinate graph, which is consistent with given mechanism.
The mechanism of esterification in presence of acid catalyst (H2SO4) is proposed as follows:
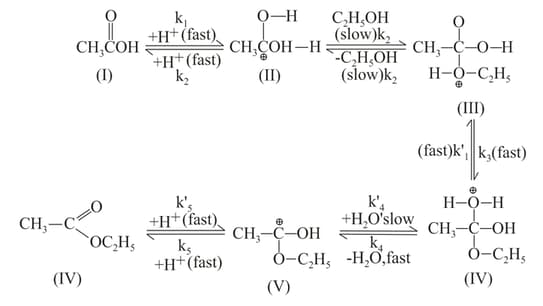
Which of the following is compound?
In the steady state approximation, if is the intermediate formed, then
The mechanism of esterification in presence of acid catalyst is proposed as follows:
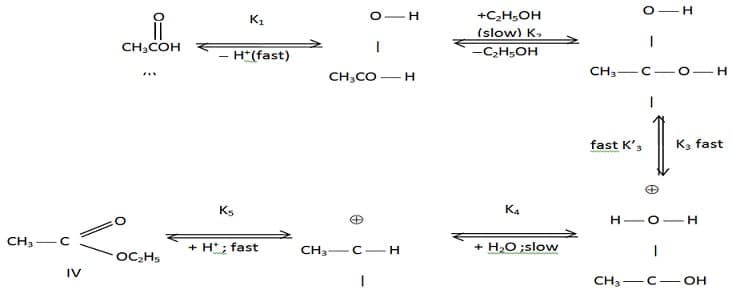
Which of the following potential energy vs reaction co-ordinate diagram is consistent with given mechanism?
STATEMENT-1:
The rate of the above reaction is independent of the concentration of CO
STATEMENT-2: The rate does not depend upon [CO] because it is involved in fast step.
A hypothetical reaction follows the mechanism as given below:
What will be the order of the overall reaction?
The reaction: has been assigned to follow given mechanism:
I.
II.
III.
The rate constant of step II is while equilibrium constant of step I is . What is the rate of reaction when concentration of and each is mole
In a multistep reaction, find out the overall rate of reaction:
Consider this reaction :
The rate law for the above reaction is given as . Which of the following mechanism is/are consistent with the rate law?
The mechanism of the following reaction is:
Step 1
Step 2
Which of the following statements is true-
As per the following consecutive reactions the r.d.s. is
(P)
(Q)
(R)
(S)
For reaction , following mechanism has been proposed and .
The following mechanism is proposed for the reaction of with to from
If the second step is considered as the rate determining step, the order of the reaction with respect to is
Select the intermediate in the following reaction:
Step (a)
Step (b)
The rate constant of one reaction is double of the rate constant of another reaction. Then the relationship between the corresponding activation energies of the two reactions ( and ) will be
Consider the following parallel reactions being given by A (t1/2 = 1.386
If distribution of A in the product mixture is 50%, calculate partial half-life of A for the conversion into B.
Give the hypothetical reaction mechanism
and the rate as
| Species found | Rate of its formation |
|---|---|
| B | 0.002 mol/h, per mole of A |
| C | 0.030 mol/h, per mole of B |
| D | 0.011 mol/h, per mole of C |
| E | 0.420 mol/h, per mole of D |
Consider the reaction,
The rate equation for this reaction is, rate
Which of these mechanisms is/are consistent with this rate equation?
A.
B.